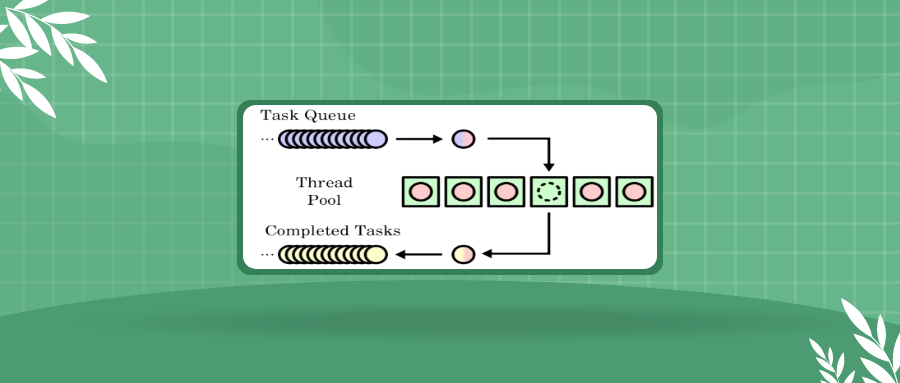
本文中关于线程池实现和编写步骤相关细节,请观看视频
手把手教你撸一个线程池 - C语言版 1. 线程池原理 我们使用线程的时候就去创建一个线程,这样实现起来非常简便,但是就会有一个问题:如果并发的线程数量很多,并且每个线程都是执行一个时间很短的任务就结束了,这样频繁创建线程就会大大降低系统的效率,因为频繁创建线程和销毁线程需要时间。
那么有没有一种办法使得线程可以复用,就是执行完一个任务,并不被销毁,而是可以继续执行其他的任务呢?
线程池是一种多线程处理形式,处理过程中将任务添加到队列,然后在创建线程后自动启动这些任务。线程池线程都是后台线程。每个线程都使用默认的堆栈大小,以默认的优先级运行,并处于多线程单元中。如果某个线程在托管代码中空闲(如正在等待某个事件),则线程池将插入另一个辅助线程来使所有处理器保持繁忙。如果所有线程池线程都始终保持繁忙,但队列中包含挂起的工作,则线程池将在一段时间后创建另一个辅助线程但线程的数目永远不会超过最大值。超过最大值的线程可以排队,但他们要等到其他线程完成后才启动。
在各个编程语言的语种中都有线程池的概念,并且很多语言中直接提供了线程池,作为程序猿直接使用就可以了,下面给大家介绍一下线程池的实现原理:
2. 任务队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 typedef struct Task { void (*function)(void * arg); void * arg; }Task;
3. 线程池定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 struct ThreadPool { Task* taskQ; int queueCapacity; int queueSize; int queueFront; int queueRear; pthread_t managerID; pthread_t *threadIDs; int minNum; int maxNum; int busyNum; int liveNum; int exitNum; pthread_mutex_t mutexPool; pthread_mutex_t mutexBusy; pthread_cond_t notFull; pthread_cond_t notEmpty; int shutdown; };
4. 头文件声明 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #ifndef _THREADPOOL_H #define _THREADPOOL_H typedef struct ThreadPool ThreadPool ;ThreadPool *threadPoolCreate (int min, int max, int queueSize) ; int threadPoolDestroy (ThreadPool* pool) ;void threadPoolAdd (ThreadPool* pool, void (*func)(void *), void * arg) ;int threadPoolBusyNum (ThreadPool* pool) ;int threadPoolAliveNum (ThreadPool* pool) ;void * worker (void * arg) ;void * manager (void * arg) ;void threadExit (ThreadPool* pool) ;#endif
5. 源文件定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 ThreadPool* threadPoolCreate (int min, int max, int queueSize) { ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)malloc (sizeof (ThreadPool)); do { if (pool == NULL ) { printf ("malloc threadpool fail...\n" ); break ; } pool->threadIDs = (pthread_t *)malloc (sizeof (pthread_t ) * max); if (pool->threadIDs == NULL ) { printf ("malloc threadIDs fail...\n" ); break ; } memset (pool->threadIDs, 0 , sizeof (pthread_t ) * max); pool->minNum = min; pool->maxNum = max; pool->busyNum = 0 ; pool->liveNum = min; pool->exitNum = 0 ; if (pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutexPool, NULL ) != 0 || pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutexBusy, NULL ) != 0 || pthread_cond_init(&pool->notEmpty, NULL ) != 0 || pthread_cond_init(&pool->notFull, NULL ) != 0 ) { printf ("mutex or condition init fail...\n" ); break ; } pool->taskQ = (Task*)malloc (sizeof (Task) * queueSize); pool->queueCapacity = queueSize; pool->queueSize = 0 ; pool->queueFront = 0 ; pool->queueRear = 0 ; pool->shutdown = 0 ; pthread_create(&pool->managerID, NULL , manager, pool); for (int i = 0 ; i < min; ++i) { pthread_create(&pool->threadIDs[i], NULL , worker, pool); } return pool; } while (0 ); if (pool && pool->threadIDs) free (pool->threadIDs); if (pool && pool->taskQ) free (pool->taskQ); if (pool) free (pool); return NULL ; } int threadPoolDestroy (ThreadPool* pool) { if (pool == NULL ) { return -1 ; } pool->shutdown = 1 ; pthread_join(pool->managerID, NULL ); for (int i = 0 ; i < pool->liveNum; ++i) { pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notEmpty); } if (pool->taskQ) { free (pool->taskQ); } if (pool->threadIDs) { free (pool->threadIDs); } pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutexPool); pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutexBusy); pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->notEmpty); pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->notFull); free (pool); pool = NULL ; return 0 ; } void threadPoolAdd (ThreadPool* pool, void (*func)(void *), void * arg) { pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool); while (pool->queueSize == pool->queueCapacity && !pool->shutdown) { pthread_cond_wait(&pool->notFull, &pool->mutexPool); } if (pool->shutdown) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); return ; } pool->taskQ[pool->queueRear].function = func; pool->taskQ[pool->queueRear].arg = arg; pool->queueRear = (pool->queueRear + 1 ) % pool->queueCapacity; pool->queueSize++; pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notEmpty); pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); } int threadPoolBusyNum (ThreadPool* pool) { pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy); int busyNum = pool->busyNum; pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy); return busyNum; } int threadPoolAliveNum (ThreadPool* pool) { pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool); int aliveNum = pool->liveNum; pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); return aliveNum; } void * worker (void * arg) { ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)arg; while (1 ) { pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool); while (pool->queueSize == 0 && !pool->shutdown) { pthread_cond_wait(&pool->notEmpty, &pool->mutexPool); if (pool->exitNum > 0 ) { pool->exitNum--; if (pool->liveNum > pool->minNum) { pool->liveNum--; pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); threadExit(pool); } } } if (pool->shutdown) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); threadExit(pool); } Task task; task.function = pool->taskQ[pool->queueFront].function; task.arg = pool->taskQ[pool->queueFront].arg; pool->queueFront = (pool->queueFront + 1 ) % pool->queueCapacity; pool->queueSize--; pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notFull); pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); printf ("thread %ld start working...\n" , pthread_self()); pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy); pool->busyNum++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy); task.function(task.arg); free (task.arg); task.arg = NULL ; printf ("thread %ld end working...\n" , pthread_self()); pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy); pool->busyNum--; pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy); } return NULL ; } void * manager (void * arg) { ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)arg; while (!pool->shutdown) { sleep(3 ); pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool); int queueSize = pool->queueSize; int liveNum = pool->liveNum; pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy); int busyNum = pool->busyNum; pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy); if (queueSize > liveNum && liveNum < pool->maxNum) { pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool); int counter = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < pool->maxNum && counter < NUMBER && pool->liveNum < pool->maxNum; ++i) { if (pool->threadIDs[i] == 0 ) { pthread_create(&pool->threadIDs[i], NULL , worker, pool); counter++; pool->liveNum++; } } pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); } if (busyNum * 2 < liveNum && liveNum > pool->minNum) { pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool); pool->exitNum = NUMBER; pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); for (int i = 0 ; i < NUMBER; ++i) { pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notEmpty); } } } return NULL ; } void threadExit (ThreadPool* pool) { pthread_t tid = pthread_self(); for (int i = 0 ; i < pool->maxNum; ++i) { if (pool->threadIDs[i] == tid) { pool->threadIDs[i] = 0 ; printf ("threadExit() called, %ld exiting...\n" , tid); break ; } } pthread_exit(NULL ); }
6. 测试代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 void taskFunc (void * arg) { int num = *(int *)arg; printf ("thread %ld is working, number = %d\n" , pthread_self(), num); sleep(1 ); } int main () { ThreadPool* pool = threadPoolCreate(3 , 10 , 100 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; ++i) { int * num = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int )); *num = i + 100 ; threadPoolAdd(pool, taskFunc, num); } sleep(30 ); threadPoolDestroy(pool); return 0 ; }
线程池C语言改C++版