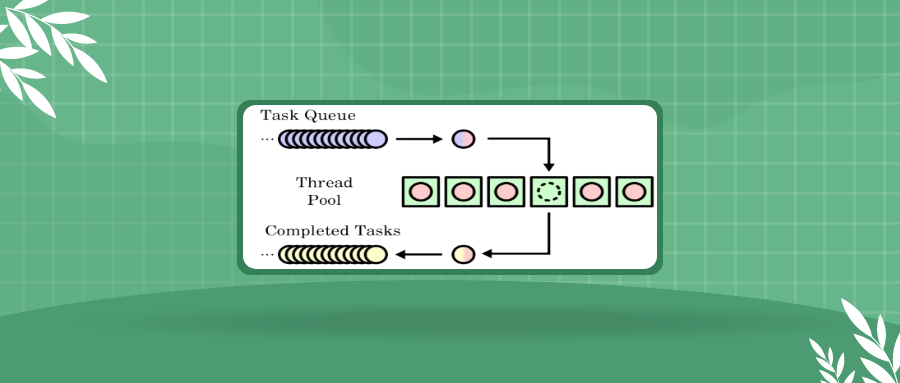
在手把手教你写C语言线程池中,已经实现了C语言版的线程池,如果我们也学过C++的话,可以将其改为C++版本,这样代码不管是从使用还是从感观上都会更简洁一些。
对这些代码做从C到C++的迁移主要用到了C++三大特性中的封装,因此难度不大,对应C++初学者来说有助于提高编码水平和对面向对象的理解,对于熟练掌握了C++的人来说就是张飞吃豆芽 -- 小菜一碟(so easy)。
关于线程的在此就不再过多阐述,对于前面文章中设计的线程池,按照面向对象的思想进行拆分可以分为两部分(纯属个人见解,有不同的想法也正常):任务队列类 和线程池类。
本文中关于线程池实现和编写步骤相关细节,请观看视频
手把手教你撸一个线程池 - C++版
1. 任务队列
1.1 类声明
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
using callback = void(*)(void*);
struct Task
{
Task()
{
function = nullptr;
arg = nullptr;
}
Task(callback f, void* arg)
{
function = f;
this->arg = arg;
}
callback function;
void* arg;
};
class TaskQueue
{
public:
TaskQueue();
~TaskQueue();
void addTask(Task& task);
void addTask(callback func, void* arg);
Task takeTask();
inline int taskNumber()
{
return m_queue.size();
}
private:
pthread_mutex_t m_mutex;
std::queue<Task> m_queue;
};
|
其中Task是任务类,里边有两个成员,分别是两个指针void(*)(void*)和void*
另外一个类TaskQueue是任务队列,提供了添加任务、取出任务、存储任务、获取任务个数、线程同步的功能。
1.2 类定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| TaskQueue::TaskQueue()
{
pthread_mutex_init(&m_mutex, NULL);
}
TaskQueue::~TaskQueue()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_mutex);
}
void TaskQueue::addTask(Task& task)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex);
m_queue.push(task);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex);
}
void TaskQueue::addTask(callback func, void* arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex);
Task task;
task.function = func;
task.arg = arg;
m_queue.push(task);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex);
}
Task TaskQueue::takeTask()
{
Task t;
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex);
if (m_queue.size() > 0)
{
t = m_queue.front();
m_queue.pop();
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex);
return t;
}
|
2. 线程池
2.1 类声明
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| class ThreadPool
{
public:
ThreadPool(int min, int max);
~ThreadPool();
void addTask(Task task);
int getBusyNumber();
int getAliveNumber();
private:
static void* worker(void* arg);
static void* manager(void* arg);
void threadExit();
private:
pthread_mutex_t m_lock;
pthread_cond_t m_notEmpty;
pthread_t* m_threadIDs;
pthread_t m_managerID;
TaskQueue* m_taskQ;
int m_minNum;
int m_maxNum;
int m_busyNum;
int m_aliveNum;
int m_exitNum;
bool m_shutdown = false;
};
|
2.2 类定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
| ThreadPool::ThreadPool(int minNum, int maxNum)
{
m_taskQ = new TaskQueue;
do {
m_minNum = minNum;
m_maxNum = maxNum;
m_busyNum = 0;
m_aliveNum = minNum;
m_threadIDs = new pthread_t[maxNum];
if (m_threadIDs == nullptr)
{
cout << "malloc thread_t[] 失败...." << endl;;
break;
}
memset(m_threadIDs, 0, sizeof(pthread_t) * maxNum);
if (pthread_mutex_init(&m_lock, NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_cond_init(&m_notEmpty, NULL) != 0)
{
cout << "init mutex or condition fail..." << endl;
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < minNum; ++i)
{
pthread_create(&m_threadIDs[i], NULL, worker, this);
cout << "创建子线程, ID: " << to_string(m_threadIDs[i]) << endl;
}
pthread_create(&m_managerID, NULL, manager, this);
} while (0);
}
ThreadPool::~ThreadPool()
{
m_shutdown = 1;
pthread_join(m_managerID, NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < m_aliveNum; ++i)
{
pthread_cond_signal(&m_notEmpty);
}
if (m_taskQ) delete m_taskQ;
if (m_threadIDs) delete[]m_threadIDs;
pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_lock);
pthread_cond_destroy(&m_notEmpty);
}
void ThreadPool::addTask(Task task)
{
if (m_shutdown)
{
return;
}
m_taskQ->addTask(task);
pthread_cond_signal(&m_notEmpty);
}
int ThreadPool::getAliveNumber()
{
int threadNum = 0;
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_lock);
threadNum = m_aliveNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_lock);
return threadNum;
}
int ThreadPool::getBusyNumber()
{
int busyNum = 0;
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_lock);
busyNum = m_busyNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_lock);
return busyNum;
}
void* ThreadPool::worker(void* arg)
{
ThreadPool* pool = static_cast<ThreadPool*>(arg);
while (true)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->m_lock);
while (pool->m_taskQ->taskNumber() == 0 && !pool->m_shutdown)
{
cout << "thread " << to_string(pthread_self()) << " waiting..." << endl;
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->m_notEmpty, &pool->m_lock);
if (pool->m_exitNum > 0)
{
pool->m_exitNum--;
if (pool->m_aliveNum > pool->m_minNum)
{
pool->m_aliveNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
pool->threadExit();
}
}
}
if (pool->m_shutdown)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
pool->threadExit();
}
Task task = pool->m_taskQ->takeTask();
pool->m_busyNum++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
cout << "thread " << to_string(pthread_self()) << " start working..." << endl;
task.function(task.arg);
delete task.arg;
task.arg = nullptr;
cout << "thread " << to_string(pthread_self()) << " end working...";
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->m_lock);
pool->m_busyNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
}
return nullptr;
}
void* ThreadPool::manager(void* arg)
{
ThreadPool* pool = static_cast<ThreadPool*>(arg);
while (!pool->m_shutdown)
{
sleep(5);
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->m_lock);
int queueSize = pool->m_taskQ->taskNumber();
int liveNum = pool->m_aliveNum;
int busyNum = pool->m_busyNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
const int NUMBER = 2;
if (queueSize > liveNum && liveNum < pool->m_maxNum)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->m_lock);
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < pool->m_maxNum && num < NUMBER
&& pool->m_aliveNum < pool->m_maxNum; ++i)
{
if (pool->m_threadIDs[i] == 0)
{
pthread_create(&pool->m_threadIDs[i], NULL, worker, pool);
num++;
pool->m_aliveNum++;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
}
if (busyNum * 2 < liveNum && liveNum > pool->m_minNum)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->m_lock);
pool->m_exitNum = NUMBER;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->m_lock);
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER; ++i)
{
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->m_notEmpty);
}
}
}
return nullptr;
}
void ThreadPool::threadExit()
{
pthread_t tid = pthread_self();
for (int i = 0; i < m_maxNum; ++i)
{
if (m_threadIDs[i] == tid)
{
cout << "threadExit() function: thread "
<< to_string(pthread_self()) << " exiting..." << endl;
m_threadIDs[i] = 0;
break;
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
|